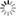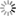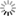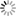Warming caused by cumulative carbon emissions towards the trillionth tonne
We find that the peak warming caused by a given cumulative carbon dioxide emission is better constrained than the warming response to a stabilization scenario. Furthermore, the relationship between cumulative emissions and peak warming is remarkably insensitive to the emission pathway (timing of emissions or peak emission rate). Hence policy targets based on limiting cumulative emissions of carbon dioxide are likely to be more robust to scientific uncertainty than emission-rate or concentration targets. Total anthropogenic emissions of one trillion tonnes of carbon (3.67 trillion tonnes of CO2), about half of which has already been emitted since industrialization began, results in a most likely peak carbon-dioxide- induced warming of 2 6C above pre-industrial temperatures, with a 5–95% confidence interval of 1.3–3.9 6C.
Credits: Nature 30 April 2009
Fair Use OK
DOWNLOAD FILE — PDF document, 838 kB (858,428 bytes)